Alabama Hospital Focuses on Infection Prevention to Decrease C. difficile Infections

Baptist Medical Center South is a licensed 492-bed hospital in Montgomery, Alabama. As an enrolled hospital in Alliant Health’s Hospital Quality Improvement Contractor (HQIC) program, the hospital teams work to improve quality and patient safety, including infection prevention.
Opportunity for improvement was identified based on data, reviews, and specimen testing:
- Infection Prevention found the standardized infection ratio (SIR) was greater than the recommended goal of <1.0.
- difficile infection (CDI) reviews found that education was needed regarding diagnostic stewardship.
- Only a Nucleic Acid Amplified Test (NAAT) was utilized for diff. Two-step testing, which includes a toxin result, was not available.
- Increased antimicrobial usage and patient’s length of stay
- Specimen integrity was a concern.
- Did it need to be tested? Was it truly diarrhea? Has the patient been on any type of laxative, tube feedings, or IV contrast in the last 24-48 hours?
- Testing ordered and specimens sent to the lab were> 48 hours apart.
- The specimen was not collected within an appropriate time frame.
- During this time, many changes can happen, potentially increasing the risk of false positives, such as tube feeding and IV contrast.
- Patients are also placed in isolation during the collection time frame. We have seen patient satisfaction decrease due to an elongated isolation time.
- Specimens collected and sent to the lab were not optimal for testing
- Many formed stools were rejected
- The specimen was not collected within an appropriate time frame.
- Only a Nucleic Acid Amplified Test (NAAT) was utilized for diff. Two-step testing, which includes a toxin result, was not available.
Initiatives:
- Two-step testing was put in place to identify active infection vs colonization.
- Hospital now tests for C diff If the NAAT is positive, the orderable will reflex to test the toxin.
- If the toxin is negative, the patient is colonized. Treatment is unnecessary, and the patient will remain isolated until symptoms resolve.
- If the toxin is positive, an active infection is indicated. Treatment would then be initiated, and IP would continue to monitor for isolation purposes.
- Only toxin + results are included in HO-c diff criteria. This initiative significantly decreased our reportable HO-c diff.
- To help ensure a high-integrity specimen was collected appropriately, IP worked with the IT and Lab departments to cancel any C diff testing not collected within 48 hours.
- The provider and nursing reassess the patient and re-order the test if needed.
- IP also implemented a diarrhea decision tree to help nurses have a tool to follow when a C diff test is ordered. See graphic.
- Hospital now tests for C diff If the NAAT is positive, the orderable will reflex to test the toxin.
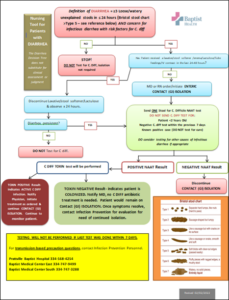
Outcomes:
Their goal was met as the number of hospital-onset C. diff significantly decreased from 2021 through 2023.
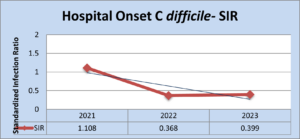
In addition, Baptist Medical Center South has maintained a Standardized Infection Rate (SIR) of <1.0 for the past two years. Increased awareness of diagnostic stewardship, contact precautions, and decreased antimicrobial usage are attributed to their performance improvement.